Controversial studies show that the frequencies that bother insects can vary greatly, ranging from infrasound to ultrasound.
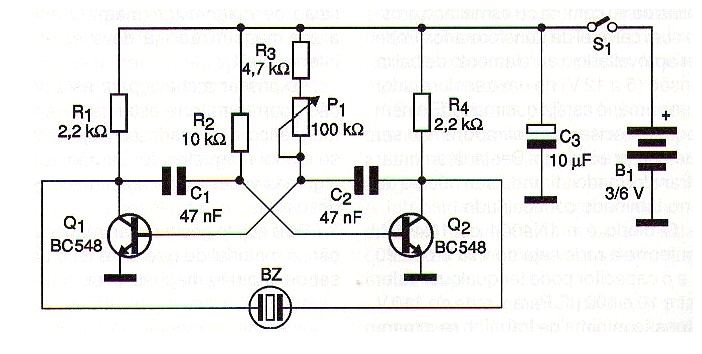
Some researchers, for example, claim that the frequencies that have the most positive effects are in the range of 2 to 7 kHz, and this is precisely the range generated by the device we describe below. A potentiometer (P1) allows the user of the device to adjust the frequency and thus experiment to find those that produce the desired effects. The circuit is quite simple and is based only on transistors, which makes it much easier for beginners or those who do not have many resources on their electronics bench to assemble. It can be powered by two or four small batteries, and since the current drawn is very small, its durability is enormous. Figure 1 shows the complete diagram of the device.
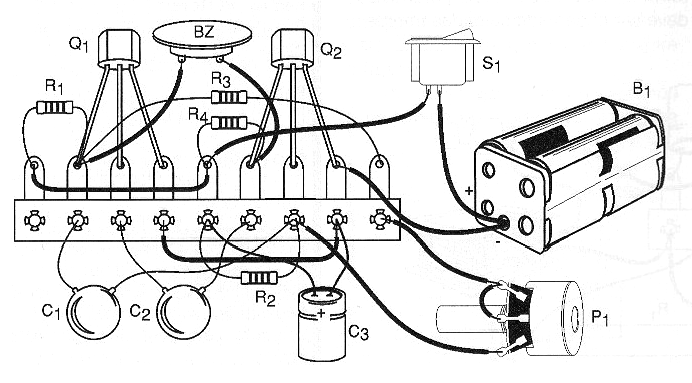
In figure 2 we have the arrangement of the components in a terminal strip which fits easily with the other elements (batteries and buzzer) in a small plastic box.
The transducer used is a ceramic piezoelectric type, a piezoelectric buzzer or equivalent, for example, a crystal or ceramic headphone capsule. The transistors accept equivalents since any general-purpose NPN will do. Even PNP types can be used by inverting the polarity of the batteries. The resistors are 1/8W and either a potentiometer or a trim pot can be used for adjustment. Capacitors C1 and C2 are polyester or ceramic, while C3 is a 6 V electrolytic whose value can be between 10 uF and 220 uF. To test the device, simply turn on the power and adjust P1 so that it emits a sound similar to that produced by the insect you want to scare away or a common buzzing insect. To use, simply leave the device on. Try different frequencies to find out which one "works".
MATERIAL LIST
Semiconductors:
Q1, Q2 - BC548 or equivalent - general-purpose NPN transistors
Resistors: (1/8W, 5%)
R1, R4 - 2.2 k ohms - red, red, red
R2 - 10 k ohms - brown, black, orange
R3 - 4.7 k ohms - yellow, violet, red
P1 - 100 k ohms - trimpot or potentiometer
Capacitors:
C1, C2 - 47 nF (473 or 0.047) - ceramic or polyester
C3 - 10 uF to 220 uF/6 V - electrolytic
Miscellaneous:
BZ - MP-10 ceramic transducer or equivalent
S1 - Single-ended switch
B1 - 2 or 4 batteries - 3 or 6 V
Terminal strip, battery holder, mounting box, pushbutton the potentiometer, wires, solder, etc.