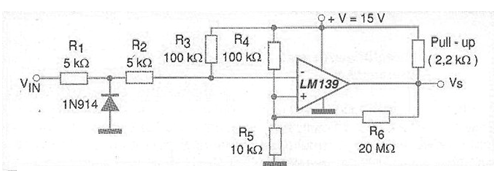
In many applications involving control of circuits from the power grid, the zero-pass detector is a key element. This is the case for phase angle power controls that make use of TRIACs and other thyristors or power devices. A zero-crossing detector is a circuit that produces an output pulse when an alternating voltage applied to its input passes through the zero-volt point. The circuit, which uses only one voltage comparator, is shown in the figure. The output signal of this circuit is a square wave that corresponds to the sinusoidal signal applied to the input. This means that it can also be used to make a sinusoidal signal rectangular. The hysteresis of the circuit is low, less than 10 mV and the power supply need not be symmetrical.