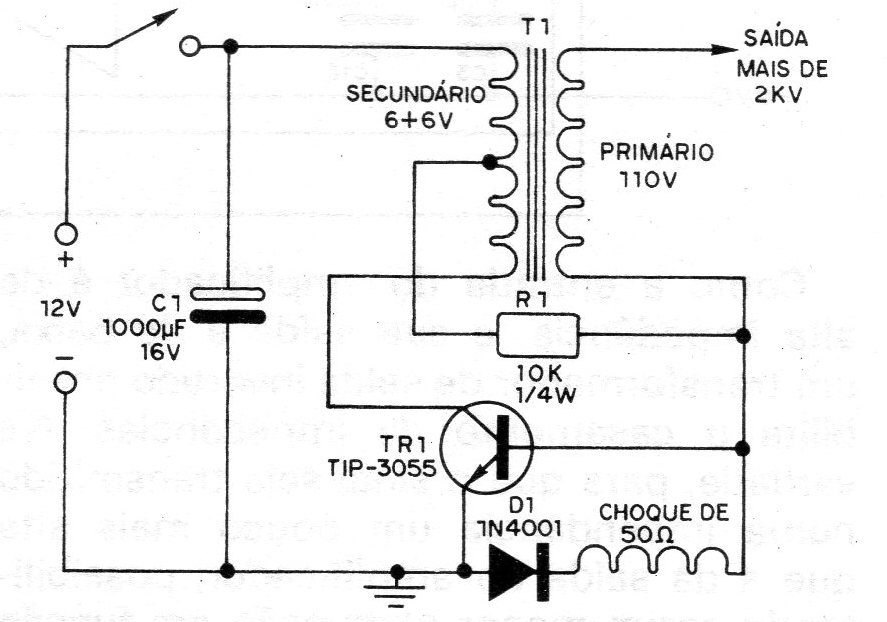
This circuit was found in a 1982 publication. From the low voltage of a 12 V battery, we can obtain a very high alternating voltage with this inverter circuit. The value of the voltage obtained depends on the type of transformer, peaks of more than 1000 V may occur in some cases. Obviously, the power transferred in this circuit is low, which means that, even with high voltage, the current is very small, and that only loads with very low energy consumption can be fed in this case. Circuits that can be powered by the inverter are therefore limited to low-power fluorescent lamps, ionizers, etc. The transformer used is of the type of supply with a secondary of 6 + 6 V and a primary of 110 V or 220 V. Of course, the primary of 220 V allows to obtain a higher voltage. The ideal operating point of the circuit is given by the value of R1, which must be achieved experimentally depending on the transformer. The TIP3055 transistor must be equipped with a heat sink.