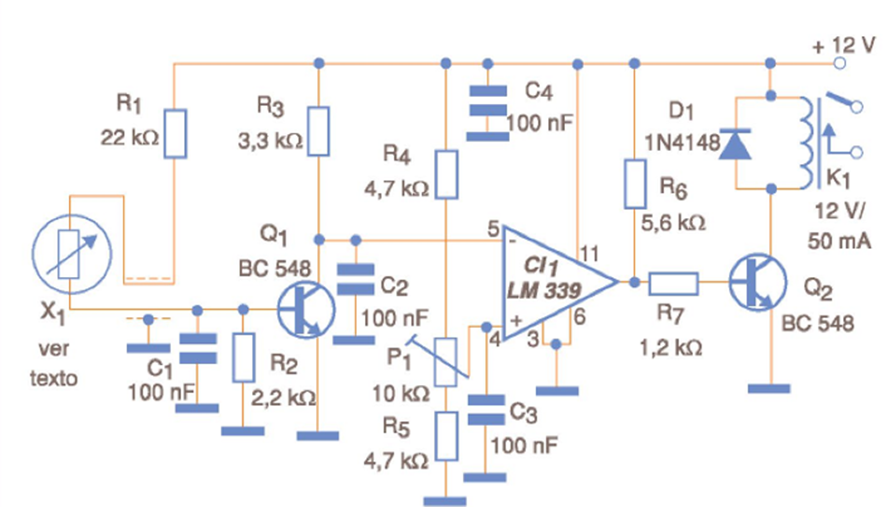
The general-purpose thermostat shown in the figure uses a high-resistive thermistor as a sensor. Thermistors in the range of 47 k ohms to 220 k ohms can be used and in their function the value of R3 must be changed to obtain the desired sensitivity and the relay trigger point. By using a transistorized amplifier stage, small variations in the thermistor resistance are detected, taking the circuit to the trigger point. The trigger point is adjusted by the trimmer connected to the comparator reference input. For greater precision, a multiturn trimmer should be used. The relay used is a sensitive type with a 50 mA coil (maximum) and voltage according to the power supply voltage. If the sensor is located somewhat far from the circuit (more than 2 meters), a shielded cable with the mesh properly grounded should be used. The 100 nF capacitor at the thermistor input prevents transients or short-duration pulses from causing the circuit to trigger erratically. The power supply must be stabilized so as not to affect the circuit's trigger point. One possibility that can be considered for some applications is to place a common reverse-biased diode as a temperature sensor.